Self-learning Knowledge Models
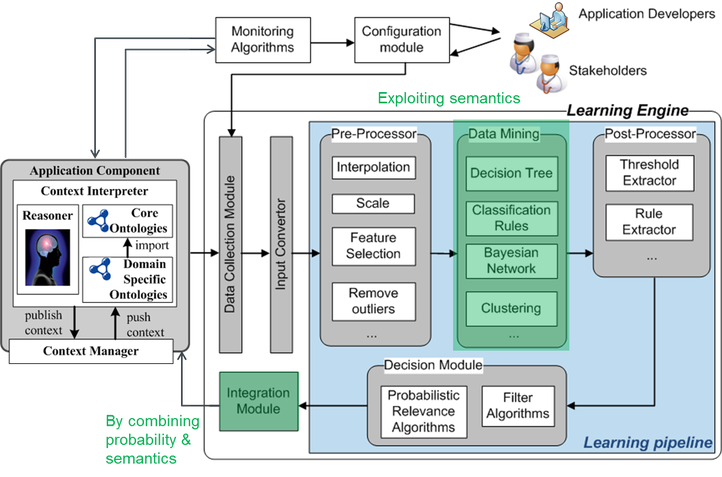
Semantic knowledge models capture the expert and background knowledge about a particular domain and involved stakeholders, e.g. user profiles, medical knowledge, context, etc. This knowledge is then exploited by applications to offer personalized & context-aware intelligent services to the end-users. However, knowledge constantly evolves and new insights should be able to be incorporated in the knowledge model. Therefore, the main research objective of this track is to devise algorithms, platforms and techniques that enable self-learning and evolving knowledge models that accurately reflect a domain.
Specifically, our research efforts focus on the following three topics:
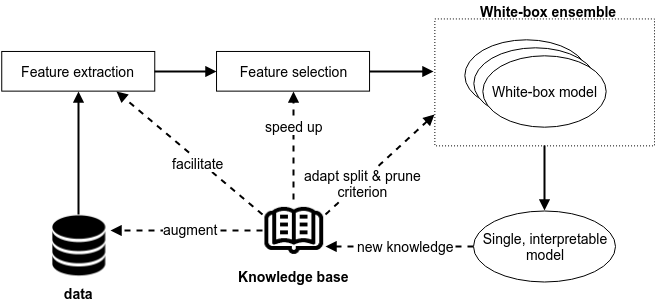
- Design of data mining techniques that allow to process and exploit the captured semantic data in order to discover new semantic links and concepts, e.g., using inductive logic programming or association rule mining.
- Design of algorithms and techniques that allow to exploit the semantics captured in knowledge models in order to improve the accuracy and performance of machine learning techniques, e.g., to boost learning speed and generalization capability, to enhance feature selection & extraction techniques, to improve model parameter initialization, etc.
- Design of platform and techniques that allow that support evolving knowledge models, supporting multiple views on a domain through probabilistic logics and reasoning.
- A participatory ontology engineering methodology that allows to accurately and incrementally construct knowledge models together with domain experts without requiring medical knowledge from them.
Staff
Filip De Turck, Femke Ongenae, Femke De Backere, Erik Mannens, Ruben Verborgh
Researchers
Pieter Bonte, Gilles Vandewiele, Rein Houthooft, Laurens De Vocht, Anastasia Dimou, Pieter Heyvaert
Projects
- ICON AORTA: Adaptive Optimization for Resource and Task Allocation in Hospitals
- ICON ACCIO:Ambient aware provisioning of Continuous Care for Intra-muros Organizations
- ICON – WONDER: interventions for Wandering and Other behavioral disturbaNces of persons with DEmentia in nursing homes by personalized Robot interactions
- Bilateral ESS: Environmental Sensing Study
Key publications
- Femke Ongenae, Maxim Claeys, Thomas Dupont, Wannes Kerckhove, Piet Verhoeve, Tom Dhaene, Filip De Turck, A Probabilistic Ontology-based Platform for Self-learning Context-aware Healthcare Applications, Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 40, Nr. 18, pp. 7629-7646, 2013.
- Femke Ongenae, Maxim Claeys, Wannes Kerckhove, Thomas Dupont, Piet Verhoeve and Filip De Turck, A self-learning nurse call system, Computers in Biology and Medicine, Vol. 44, Nr. 1, pp. 110-123, 2014.
- Pieter Bonte, Femke Ongenae, Filip De Turck, Learning semantic rules for intelligent transport scheduling in hospitals, In Proc. of the Extended Semantic Web Conference (ESWC), Heraklion, Greece, Mag 29 – June 2, 2016.
- Pieter Bonte, Femke Ongenae, Filip De Turck, Mining semantic rules for optimizing transport assignments in hospitals, In Proc. of the International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC), Kobe, Japan, 17-21 October, 2016.
- Rein Houthooft, Cedric De Boom, Stijn Verstichel, Femke Ongenae, Filip De Turck, Structured output prediction for semantic perception in autonomous vehicles, In Proc. of the 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, Arizona, USA, 12-17 February 2016.
- Femke Ongenae, Duysburgh, P., Sulmon, N., Verstraete, M., Bleumers, L., De Zutter, S., Verstichel, S., et al. (2014). An ontology co-design method for the co-creation of a continuous care ontology. APPLIED ONTOLOGY, 9(1), 27–64.