Sustainable pyrometallurgical processing routes
One of the challenges nowadays is the increasing demand of precious and valuable metals because of the digitization of our fast developing society. The production of novel electronics and modern green energy require a lot of these precious metals which increases their demand and costs significantly and makes them even more scarce. In order to keep up with the demand, recycling of old electronics and devices will become more important in the future. For this reason, research is required regarding new processes of recycling old materials in an efficient and environment-friendly way.
Focus is put on fundamental knowledge of pyrometallurgical processes which are able to extract precious metals from waste products at industrial scales. Research is done by replicating the extreme conditions which occur during the recycling process where temperatures can reach up to over 1200°C. This is done in a controlled way by combining a lab scale set-up, which allows us to closely study the interaction of molten metals, gasses and liquid oxides at these extreme temperatures, and modelling, of both thermodynamics and microstructural evolution. Improving the knowledge of the chemistry which occurs here contributes to a better understanding of how future processes should be designed and how we can make current processes more efficient, safe and lower their impact on the environment.
Influence of multivalent ions on the electrical conductivity of slags
Pieter-Jan Boeykens, in cooperation with Umicore
One way to maximize the metal yield from both extractive and recycling pyrometallurgical processes is to minimize metal losses throughout the process. Earlier research from our department showed (also on this page) that metal losses in the slag phase are inherent to the production process. Since such slags are typically used in the building industry as concrete, the valuable metals are lost. To prevent this, an additional decantation step via an electrical resistance furnace in the production process could be added. Since such furnaces rely on Joule heating via the slag’s resistance, the ability of such a slag to carry an electrical current or the slags electrical conductivity is extremely important in the furnace design.
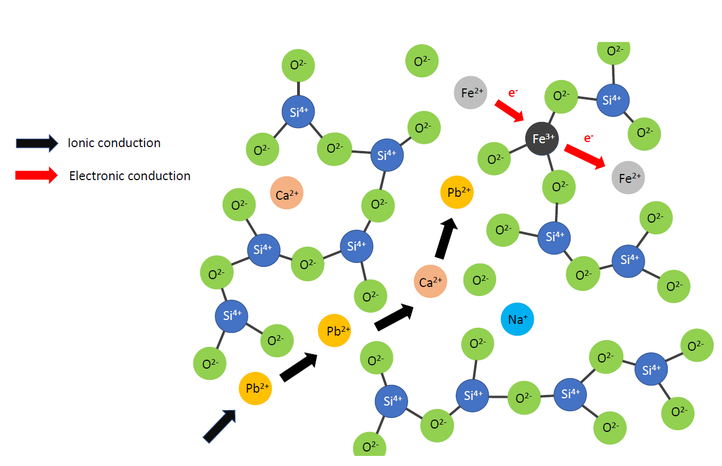
Chemically, a slag is an ionic liquid composed out of a SiO2 polymer network which is broken up by other metal oxides such as CaO or PbO. Within such a slag, the current is carried by the cations resulting in ionic conduction. However, in the presence of multivalent metals such as iron (Fe), electronic conduction is present as well via hopping of electrons. This second contribution is far less understood though and thus this will be the main focus of this research.
During this PhD, data will be obtained via an experimental setup which will be constructed in our laboratory. This conductivity setup will use a four electrode technique to prevent inaccuracies due to polarization effects and cable resistances. The total conductivity will be measured via determining the slag resistance using an AC current. Second, the ionic and electronic contribution will be separarted from each other via Stepped Potential Chronoamperometry. The oxidation state of the multivalent ions will be characterised via in situ measurement of the partial pressure of an oxygen probe and post measurement chemical analysis via Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) in combination with Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (EPR) and/or X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). From the experimental observations, a model will be constructed which can be used in the design of electrical furnaces and thus contributing to more efficient pyrometallurgical processes.
Influence of solids on slag rheology
Olivier Vergote, in cooperation with Umicore
Viscosity is one of the most important physicochemical properties during slag processing. With recycling process feedstocks becoming more complex every day, accurate predictions of slag viscosity are key for optimal process operation. Adequate predictions for fully liquid slags are nowadays available in commercial thermochemical software. However, in reality mostly solid-bearing slags will be encountered in industry. The rheology of these heterogeneous slags is not well understood and is the main research topic of this PhD.
Slag viscosity measurements will be performed in a state of the art high temperature rheometer. Both the potential of rotational as oscillating measurement modes will be examined to characterize the slag’s rheology. The obtained data will be used to asses current models which predict heterogeneous slag viscosity and enhance their model parameters.
Interaction between hot pyrometallurgical phase and coolant
Arne Simons, in cooperation with Umicore
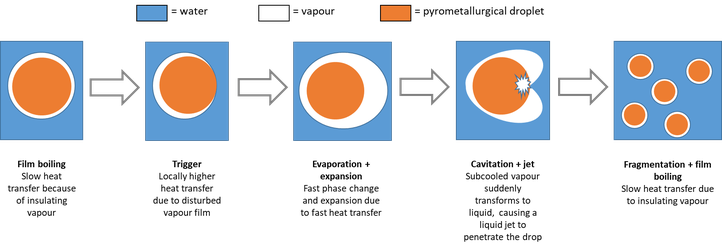
To increase the speed and the capacity of pyrometallurgical processes, temperature control is very important. To handle a pyrometallurgical phase, it should be cooled at the end of the process. Also, to increase the sustainability of the furnaces and to enhance to operating conditions of the employees, furnace cooling is needed. Both these examples use water as a coolant, but the interaction between a molten pyrometallurgical phase and water can be rather energetic, causing the rapid formation and expansion of vapour. The rate of this phenomenon increases with the contact surface, which increases as a result of the reaction itself. Hence, a chain reaction occurs that causes a sudden release of a large amount of energy, as shown in the figure below.
Schematic illustration of the chain reaction during the interaction between a pyrometallurgical phase and water
This behaviour is investigated experimentally: a droplet of the molten pyrometallurgical phase is dropped into a large volume of coolant. The interaction is then observed with a high-speed camera and a hydrophone to study the interaction for different compositions at different temperatures. The investigated parameters include melt mass, temperature and composition. Thus far, a standard method for experimenting and analysing has been developed, as it appears that[AS1] the droplet configuration might have an influence on the explosive behaviour.
These experiments will help in understanding why and how rapid vapour formation occurs, and how to avoid it. This knowledge will then be used to model the interaction between a pyrometallurgical phase and a coolant, as a predictive tool.
Convertor slag properties and their influence upon steel refining (finished project)
Lotte De Vos, in cooperation with ArcelorMittal Gent (Concluded, interesting papers can be found at the end of this section)
"Make the slag and the steel will make itself" is an old phrase in steelmaking. Slags are liquid oxide phases, which play an important role in many pyrometallurgical process. This is also the case in the convertor process. The convertor process is a necessary step in the steel production. During this process carbon, phosphor and other impurities present in the 'pig iron' from the blast furnace are removed and steel is produced. This steel is tapped from the convertor and further refined, next cast, rolled and further finished.
In a convertor, the hot liquid pig iron from the blast furnace is charged together with scrap and oxygen is blown on it. During the process, two main phases are present in the convertor: the liquid metal phase and the slag phase. This slag phase plays an important role in refining the metal phase (removing C, P, Si, etc.) but a good slag will also protect the installation from damage that could be caused by the inherent interactions at high temperatures.
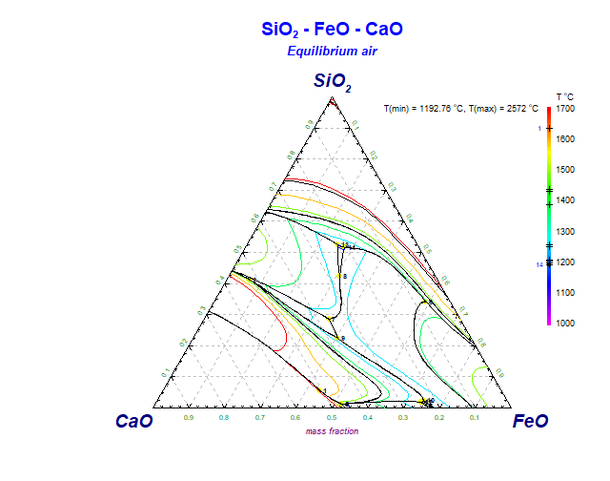
Even though there is general agreement on the importance of the slag and its functions in steelmaking, a profound and complete understanding of slags has not been reached yet. Gaining insight in the process, the working principle and the interaction between the slag and metal phase is rather difficult since a convertor is in reality a 'black box'. Thermodynamic modelling of the process is a possibility to gain insight and gather more knowledge about the process. The goal of this PhD is to apply thermodynamic models and calculations upon industrial convertor process, in order to gain fundamental knowledge and understanding of the slag phase.
Al2O3-CaO-SiO2 calculated polythermal liquidus projection. The yellow points on the diagram indicate four phase intersection points with liquid Slag. The accompanying temperatures are indicated on the temperature scale.
Interesting papers:
Slag foaming during copper smelting
Vincent Cnockaert, in cooperation with Umicore and KU Leuven (interesting papers can be found at the end of this section)
The use of liquid bath furnaces has shown to be an energy efficient and environmentally friendly way for both the primary and secondary production of non-ferrous metals such as lead, nickel and copper. Typical for these kinds of furnaces is the injection or generation of reactive gasses which occurs below the surface of the liquefied feed material. The large amount of rising gases during processing can cause foaming of liquid slag, as illustrated in the schematic below.
This slag phase is in most cases present as the upper layer of the liquid bath. The formation of excessive amounts of slag foam can hinder the production and lower the available capacity of existing smelting and converting furnaces. It is thus important to control this phenomenon and keep foaming to a minimum. It is generally accepted that the formation of slag foam is caused by a combination of a large amount of rising gases and the inherent foam stability of the slag, which in turn depends on the physical properties of the liquid slag. These causes are studied on a fundamental level. Foaming stability is modelled using novel computer simulations, supported by experiments. The generation of gasses is studied by investigating the behaviour of liquid slags to absorb and release oxygen gasses. These gasses can be absorbed over a large period of time and suddenly be released afterwards which contributes to the large amount of rising gases and thus slag foaming during copper smelting.
Interesting papers:
Microstructural evolution during pyrometallurgical processes (finished project)
Inge Bellemans, in cooperation with KU Leuven (Concluded, interesting papers can be found at the end of this section)
Many experiments are needed to investigate the influence of all parameters and, even though the microstructure and composition can be investigated. Moreover, it is very difficult to study the effect of each parameter individually because it is virtually impossible to keep the others constant. Hence, it is not straightforward to reveal the underlying chemical and physical phenomena with experiments. The phase field method already proved to be a very powerful and versatile modelling tool for microstructural evolution, e.g. during solidification, solid-state phase transformations and solid-state sintering.
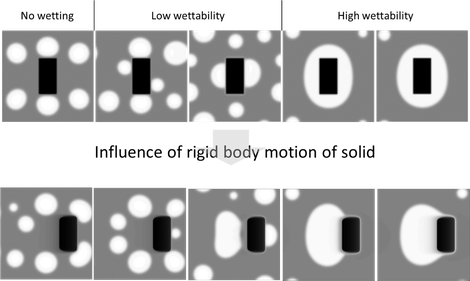
A binary phase-field model simulates the attachment of liquid metal droplets to solid particles in liquid slags with a non-reactive solid particle. The influence of several parameters on the attachment of the metal droplets to the solids was investigated: the interfacial energies, the particle morphology, initialization method, solid particle movement and the speed of the solid particle movement. Depending on the interfacial energies, four regimes were observed: no wettability of the metal on the particle, low wettability, high wettability and full wetting, as illustrated in the upper part of the figure below.
Afterwards, it was investigated how rigid body motion of the solid particle influences the attachment, as shown in the lower part of the figure below. A major observation is the fact that the apparent contact angle of the metal is larger when rigid body motion is present, which corresponds to a lower apparent wettability. The study on the influence of the speed of the rigid body motion also showed that there is a trade-off between the attraction of the metal towards the solid particle and the speed of the movement of the solid particle.
Influence of rigid body motion on the attachment of metal droplets in different wetting cases
The model was also extended to consider realistic microstructures based on actual micrographs. The origin of the attachment was investigated by comparing the two initialization methods for the metal droplets. One initialization corresponds to a case where the droplets are formed by a chemical reaction with both the droplets and the spinel solids involved. The other initialization corresponds to a situation where the droplets and particles are formed independently and are then mixed in the slag.
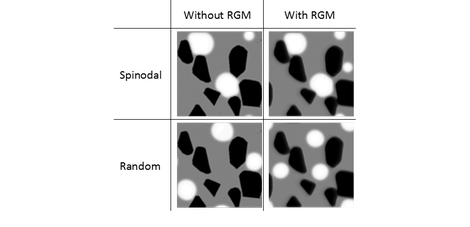
In the non-wetting case, the spinodal initialization gave microstructures corresponding best with the experiments, but in the low wettability case, the simulations of both initializations correspond well with the experimental system. The figure below illustrates simulations based on real micrographs with the two initialization methods and absence and presence of rigid body motion. The simulations for the spinodal initialization correspond better with the experimentally observed micrographs.
Comparison of simulations with spinodal (top) and random (bottom) initialization in the absence (left) or presence (right) of rigid body motion (RGM) for a realistic solid microstructure in an extreme low wetting case
Interesting papers:
- 10.1016/j.commatsci.2015.03.019
- 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.08.074
- 10.1016/j.commatsci.2016.03.022
- 10.1007/s11663-017-1088-4
- 10.1007/s11663-017-1051-4
- 10.1080/10408436.2017.1397500
- 10.1016/j.cis.2017.08.001
- 10.19150/mmp.8290
- 10.1007/s40831-017-0145-1
Interaction of solids and liquid metal in liquid slag (finished project)
Evelien De Wilde, in cooperation with Umicore and KU Leuven (Concluded, interesting papers can be found at the end of this section)
Metal losses in slags occur in pyrometallurgical production processes and limit the overall process efficiency. The metal losses are generally subdivided in two types: chemical losses referring to dissolved copper in the slag and mechanical losses referring to entrained copper droplets in the slag. For the mechanical losses, several causes can be found, one of them being the attachment of metal droplets to spinel particles in the slag. The spinel particles hinder the sedimentation process of the metal droplets. However, no fundamental understanding of this phenomenon is available.
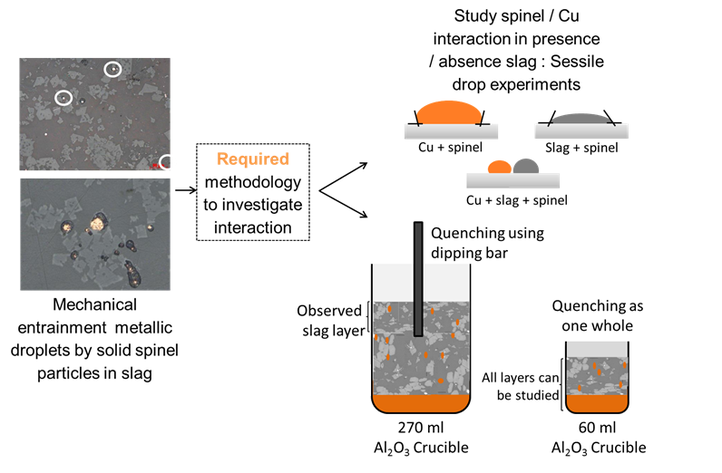
First, a suitable methodology was developed, consisting of two complementary approaches, as illustrated in the figure below:
- The different interactions (copper-spinel, slag-spinel and slag-copper-spinel) were studied in separately by a sessile drop methodology.
- The complete system (metal-slag-spinel) was also studied during smelting experiments: for this, two experimental set-ups were developed to study the attachment of copper droplets to spinels in the slag. One set-up allowed studying the influence of the sedimentation time, while the other one allowed an evaluation as a function of the slag height.
Applied methodology to investigate attachment of metal droplets to solid particles in liquid slags
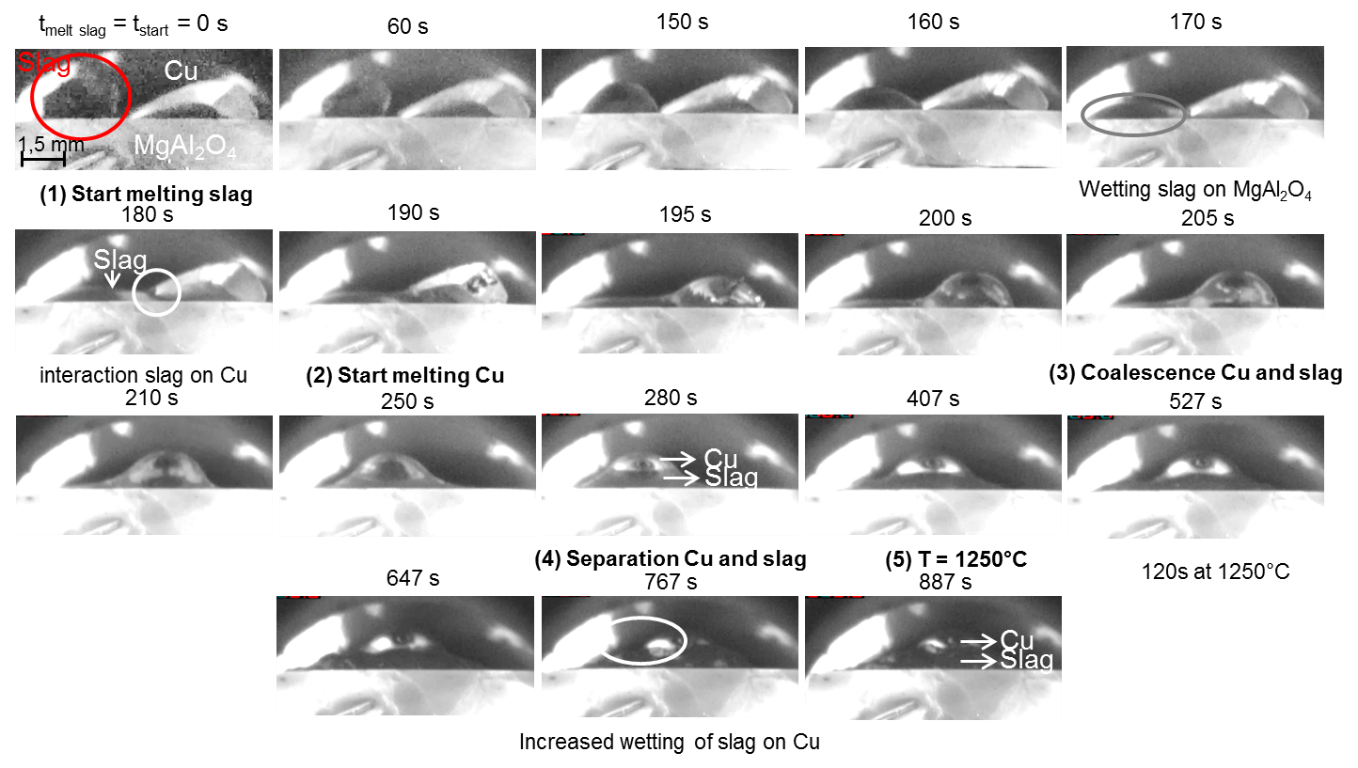
In a sessile drop experiment, both metal and slag were melted down on top of a spinel substrate, as shown in the figure below. The slag displayed a very good wetting behaviour on the spinel substrate, whereas the copper alloy drop did not wet the spinel substrate. During the experiment, the slag moved towards the alloy drop and coalescence occurred, after which the slag positioned itself between the substrate and the alloy drop. Thus, no direct interaction between the copper and the spinel substrate was possible.
Images captured during the high-temperature sessile drop experiment with metal and slag on top of a spinel substrate.
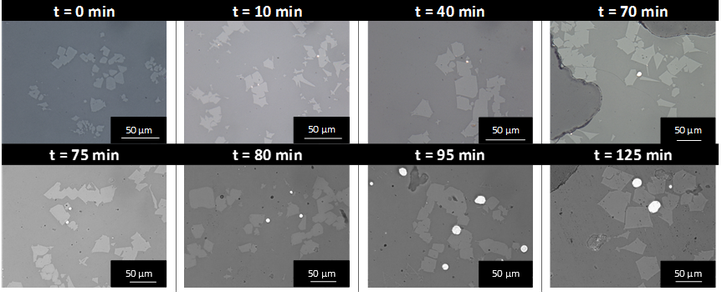
Small entrained copper droplets sticking to spinel solids were present within the slag droplet. It was suggested that during the coalescence phase in the experiment, some small Cu droplets are dispersed within the large slag drop. These droplets then act as nucleation sites for a simultaneous growth of the copper droplet and formation of a spinel solid. This leads to copper droplets attached to spinel solids within the slag phase. Also, a smelting experiment was conducted in the Fe-Si-Al-O system with Cu-Ag droplets. During the experiment, the system was first oxidized so that the copper could dissolve in the slag. This was followed by reducing the system to lower the copper solubility in the slag in turn and favour precipitation of Cu-droplets, either attached to solid particles or on their own. The amount and size of copper droplets and spinel particles increase during the complete experiment, as illustrated in the figure below.
Optical images from the samples taken during the high-temperature oxidation (upper part) and reduction part (lower part) of the experiment.
During the oxidation part, the blowing of the gas through the slag phase disturbs the underlying alloy layer. This introduces small metal droplets into the slag phase. During the oxidative part of the experiment, iron oxide has a tendency to shift towards Fe2O3 and the metallic copper is oxidized. During the reductive part of the experiment, a lack of oxygen becomes apparent and because copper is more noble than iron, Cu2O acts as oxygen donor for the oxidation of iron oxide, thereby precipitating metallic copper: 2FeO + Cu2O <-> 2Cu0 + Fe2O3. The resulting increase of Fe2O3 leads to the formation of magnetite spinel particles by reaction with FeO. These spinel solids grow at the side of the Cu-droplets, leading to copper droplets attached to spinel solids within the slag phase.
Interesting papers: