Rankings of universities
What?
Rankings are league tables of universities. On the basis of a number of parameters is each institute awarded a score which hides a much more complex profile.
One's ranking position is largely subject to the chosen parameters, the weight attributed, the statistical method used to process this data, and the reliability of the source data. For example, by changing the parameters or attributing a different weight to them, one can easily wipe the floor with any ranking. The global score however is only slightly relevant for individual output in research or education; for spearheads of research within the university, or for its scale.
Ghent University recognises the reality of rankings but does not deliberately strive for high ranking positions. A good position is the result of an internal focus on quality and excellence.
How does Ghent University perform in the rankings?
The Belgian universities get a first-rate ranking on a global scale. The largest Belgian institutes, including Ghent University, are often present in the top-200 of more than 17.000 institutes for higher education of the world.
Most prominent rankings and their methodology
Academic Rankings of World Universities
Since 2003, the Chinese Shanghai Jiaotong University presents an annual Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU). For this ranking, 1,200 higher education institutions are compared. Criteria include the number of Nobel Prizes won by alumni and professors, the number of top publications and the number of frequently cited researchers.
Leiden Ranking
Each year, the Centre for Science and Technology Studies (CWTS) publishes the Leiden Ranking, a ranking of universities according to the quality of their academic research. The Ranking is based on data from the Thomson Reuters’ Web of Science database. The results show how many publications from a certain university are in the top 1%, 10% or 50%.
U.S. News Best Global Universities Rankings
Since 2014 the American journal U.S. News started publishes a worldwide ranking list of universities based on data from Thomson Reuters’ Web of Science. In addition to the reputation among academics (25%), the research performance derived from the Web of Science (65%) and the number of PhDs awarded (10%) are also taken into account.
Times Higher Education (THE) World University Rankings
Times Higher Education (THE) has published the THE World University Rankings since 2004. This ranking is based on thirteen indicators divided in 5 categories with different weights: teaching (accounting for 30% of the score), research (30%), citations (30%), international outlook (7,5%) and industry income (2,5%). Besides data provided by the institutions themselves and bibliometric data from the Scopus database, the ranking is also largely based on a reputation survey among international scholars and employers.
QS World University Rankings
The QS World University Rankings is an annual ranking list of approximately 900 universities selected from a total of around 3500. The Ranking is compiled on the basis of a reputation survey among a large number of academics (accounting for 40% of the score) and a study among employers (10%). The ranking also takes account of the staff-student ratio (20%), citations (20%), and the percentage of international faculty (5%) and international students (5%).
The QS Sustainability Ranking assesses universities for their impact on environmental and social change. The ranking is based on metrics in two categories, environmental impact and social impact, with each contributing 50 percent of an institution’s score. Each category contains multiple sub-indicators. The environmental impact category aggregates three sub-indicators: sustainable institutions, sustainable education and sustainable research. The social impact category aggregates five sub-indicators: equality, knowledge exchange, impact of education, employability and opportunities, and quality of life.
U-Multirank
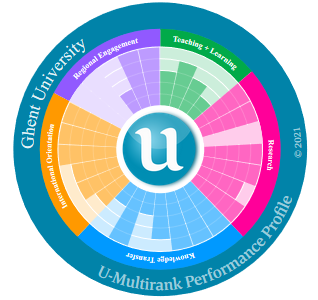
Since 2017 Ghent University has actively participated in the edition for the institutional ranking but not for the subject rankings.
The results show that for 2022, compared to the average higher education institution, Ghent University is assigned an A score (= highest score) for 15 out of 43 indicators. These top scores give a clear picture of Ghent University's strengths within the various dimensions. The provisional last results of this ranking were published in June 2022 and no data collection for a next edition took place in the same year. We received the message that the current funding period of the project was coming to an end and that the continuation of the project is being considered.